|
 |
| Home | Our Story | Articles | Products | Contact us | Hebrew |
Conditions
Products
|
Antibiotics - Replacements from Nature
Improving Physical Function & Activity
|
| Viruses | |||||||||
|
|||||||||
|
|||||||||
| What is the Virus History The Damages of Viruses The Structure of the Virus Types of Viruses The spreading of viruses Treatment and Fight against Viruses |
|||||||||
| What is the Virus | |||||||||
| The origin of the name virus in Latin, and based on a word that means poison. | |||||||||
| It is a microscopic parasite that is completely dependant on the organism's living cell host. Outside the cell its existence is without activity and it cannot reproduce. Only when it penetrates the hosting cell – the hosting cell's systems enable its reproduction. | |||||||||
| Outside of the hosting cell the virus is considered an inanimate object. But after it enters the hosting cell, the opinions are in disagreement regarding its definition. However, most scientists do not consider it to be a living organism, since it lacks systems which enable independent living. | |||||||||
| History | |||||||||
| Viruses exist anywhere living creatures are found. They probably existed from the dawn of the history of living creatures, but there is no proof for that, since they do not leave fossils behind. Their gradual discovery took place in the late 19th century until the beginning of the 2oth. During the last hundred years more and more viruses are isolated, such as the A.I.D.S. virus (HIV), which was isolated in 1983. | |||||||||
| The Damages of Viruses | |||||||||
| The attacked host reacts through inner cellular mechanisms and through its immune system, in order to rid itself for the intruder. This is frequently costs the heavy price of causing intentional self-damage to the virus-carrying cells. | |||||||||
| A significant part of the viral diseases symptoms originates from the immune system's reaction to the virus and not from the virus's attack itself. | |||||||||
| Even more so, in the last years is has been discovered that many chronic diseases originate from an autoimmune process that develops as a result of an infection, and in many cases that infectious factor is a virus. | |||||||||
| Top of Page | |||||||||
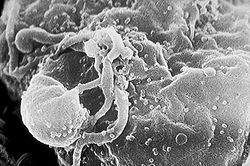
| The Structure of the Virus | |||||||||
| The virus is a microscopic-sized particle, composed of a molecule which contains a nucleus acid – RNA or DNA (genetic material), wrapped with proteins and a protein cortex. | |||||||||
|
|||||||||
| The virus is 100 times smaller than a germ | |||||||||
| Types of Viruses | |||||||||
| The viruses are divided into three groups – according to their hosting body: | |||||||||
|
|||||||||
| The spreading of viruses | |||||||||
| In case of a flue – with every cough of sneeze – millions of viruses are distributed into the air, until the next victim breaths them into their body. | |||||||||
| The virus cannot move independently, it relies on the medium – the air or blood circulation. It moves with it and randomly comes across another living cell's cortex, to which is sticks and then penetrates. | |||||||||
| Treatment and Fight against Viruses | |||||||||
| Antibiotics are useless against viruses. The germs' cells are bio chemically different from the virus's cells, which requires the taking of different types of biochemical-qualitative drugs. Taking antibiotics against a viral disease not only does not help fight the disease itself, but it helps the germs in or body develop a resistance against in, and reduces our future recovery potential through the same type of antibiotics. |
|||||||||
| There are only a small number of anti-viral drugs, since it is hard to develop medicine for their use of the hosting cell mechanisms. | |||||||||
| The defence strategy against viruses is the vaccination strategy | |||||||||
| The world's first vaccines were made by the Chinese. Children were vaccinated against small pox by inhaling a powder that was made of patients' dry, blister crusts hundreds of years ago. | |||||||||
| This strategy has proved itself effective in fighting against plagues such as small pox, polio and the measles. | |||||||||
| However, we have not yet found an efficient vaccine for diseases such as the flue, A.I.D.S., and today's newest threat – the N1H1 flue – due to the virus' amazing ability to change quickly and make the vaccine irrelevant. | |||||||||
| Modern medicine saves lives, but the under risk factor is the population which has a naturally weak immune system, such as cancer patients, organs implanted individuals and more. | |||||||||
| As mentioned, our natural defence against the hazards of the flue – including N1H1, is through our natural immune system. The more we contribute to it's strengthening every day, the more we will also strengthen out coping ability against the viruses. | |||||||||
| This is what I did - I have rebuilt my immune system with the help of Siberian Ginseng - Eleuthero | |||||||||
| Click to the Price Comparison for ordering Siberian Ginseng - Eleuthero | |||||||||
| *** In case other drugs are being taken, consult a doctor before use | |||||||||
| Top of Page |
| Home | Our Story | Articles | Products | Contact us | Hebrew |