|
 |
| Home | Our Story | Articles | Products | Contact us | Hebrew |
Conditions
Products
|
Antibiotics - Replacements from Nature
Improving Physical Function & Activity
|
| Free Radicals | |||||||||
|
|||||||||
|
|||||||||
What are Free Radicals and How are They Created |
|||||||||
| What are Free Radicals and How are They Created | |||||||||
| It is clear that all of our systems – including the immune system – need 'fuel' – food – in order to function properly. | |||||||||
| Every cell in our body requires its food to maintain structure and function in its most perfect status. | |||||||||
| Our symptoms of aging, disease and the likes are not in fact ours – they are the aging and illness of our cells. | |||||||||
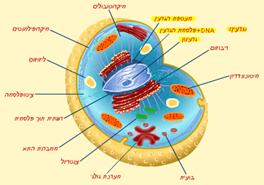
| Every cell in our body is a complex, sophisticated machine that functions at all times. | |||||||||
|
|||||||||
| Metabolism and energy-production procedures are performed in the cell at all times. | |||||||||
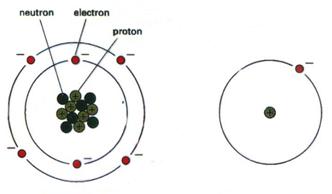
| Every substance, including living cells, is made out of atoms. | |||||||||
| Top of Page | |||||||||
| The Atomic Structure: | |||||||||
|
|||||||||
| The atoms are connected through various chemical procedures that produce complexes – molecules – which are the main components of all the substances in nature. | |||||||||
| A healthy, functioning cell is one in which the chemical procedures and reactions are performed normally, with all its atoms and molecules intact. The cell can then divide itself – thus keeping our bodies young and immune against various illnesses. | |||||||||
| The Creation Process of Free Radicals | |||||||||
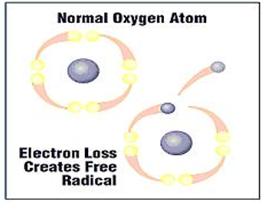
| The problems in our body occur when the chemical reactions and procedures in the cell are damaged – thus causing the release of electrons from atoms and/or molecules. | |||||||||
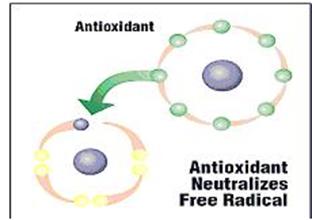
| As a result, the atoms and molecules are now missing electrons and are electrically imbalanced – these particles are referred to as free radicals. | |||||||||
|
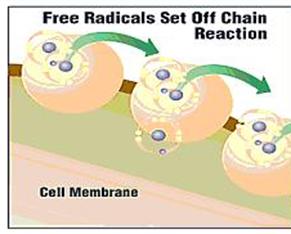
| Due to this, a chain of extremely fast reactions occur, in which the attacked molecule, which has now lost its electron, now becomes the attacker, in its quest to regain the missing charge. The molecule that it attacks becomes a new free radical, and so on in a series of reactions that cause great damage to cells and live tissues. | |||
| This procedure of "stealing" an electron by the free radical is called oxidation. For instance, the dark shade that the apple turns when it is cut open and exposed to the air is another expression of oxidation. |
|||
| There many uses in the industry with these types of substances –imbalanced, highly reactive elements such as fuels and oxygen water – substances that are designed for immediate attack – and we too can feel their actions and reactions. | |||
|
|||
| Even in our bodies, several types of free radicals are created, mainly oxygen radicals, created as a natural side-product of cell breathing procedures. These radicals serve important roles in our body, such as destroying bacteria and create connection between collagen fibers of the skin tissue, but they are also, apparently, in charge of the aging process. | |||
| In the body are also found, on a natural basis, antioxidant enzymes, which are in charge of concentrating the free radicals and to prevent them from damaging the body. | |||
| Top of Page | |||
| How Do Free Radicals Hurt Our Body | |||
| When in a status of imbalance, the free radicals will attack the proteins, oxidize fats in the body and turn them too into free radicals; they will degenerate the brain cells' mitochondria, damage the cells' membranes and reduce its ability to absorb food materials and to expel waste, and may also change the structure of its DNA. By doing so they cause early deterioration, degradation and aging of the body. It is assumed that a large number of illnesses are connected with these processes, including cancer. | |||
| This means a large number of free radicals, that is higher than that of antioxidants in the body, cause the destruction of the body. They attack the cells and destroy their function – thus causing illnesses and accelerate aging. | |||
| How do Free Radicals Get Inside Our Body | |||
|
|
|||
| Important: when there is a positive balance in the body – i.e. a quantitative advantage to the antioxidants – the body is vital and healthy in its function and the free radicals also serve their purpose without damaging it. | |||
| That is why it is important to maintain a sufficient, daily consumption of antioxidants. | |||
| Since our digestive system's absorbing capabilities are limited – even with perfect nutrition, it is advised to consume food supplements. | |||
| What is an Antioxidant? | |||
|
|||
| Top of Page | |||
| Examples for Antioxidants' Vitamins and Minerals | |||
| Vitamin A, vitamin C, vitamin E, superoxide-dismutase, flavonoids, beta-carotene, glutathione, selenium, and zinc. | |||
| I have found the best site with an amazing deal of "Buy 2 get 3 Free" !!!! or 1+1 with real low prices and very good quality products. | |||
To |
|||
| Where do Antioxidants Come From? | |||
|
|
|||
| The main and most important sources to improve your immune system by are vitamins and minerals as specified above, and antioxidants | |||
| Top of page |
| Home | Our Story | Articles | Products | Contact us | Hebrew |